. Why are we looking into this?
- Promoter Buying
- Shipping Data
- Stock making a base
- Capacity Expansion
History
In 1981, Pasuhak started the commercial manufacturing of phosgene with 1400 MT capacity. The company expanded the capacity for the first time after 33 years to 4800 MT translating to 3X increase in capacities. However during 2014 to 2022 the capacity expansion was proposed to increase the capacity by 5X from 4800 MT to 14,400 MT.
- 1968: Began operations; focus on agrochemicals; later introduced phosgene derivatives at Panelav.
- 1972: Incorporated as Paushak Limited (public company).
- 1981: Commissioned phosgene plant; progressively diversified into downstream derivatives.
- Aug 2020: Approval received to expand phosgene capacity from ~4,800 tpa to 14,400 tpa (environmental/industrial permission).
- FY20–FY24: Brand/portfolio upgrades; debottlenecking and MPP (multi‑purpose plant) additions; modernization and EHS system strengthening.
- FY25–FY26 (ongoing): New multipurpose plant and advanced R&D centre under commissioning; continued downstream capacity additions (capex program, see Section 5).
- Aug–Oct 2025: Board approved 1:2 stock split and 3:1 bonus issue; record date: 3 Oct 2025.
Major milestones such as acquisitions are not disclosed in public filings. No strategic M&A reported.
Business Overview
Paushak Limited was established in 1968 at Panelav (Halol), Gujarat and is involved in phosgene‑based specialty chemicals (phosgene gas and downstream derivatives such as chloroformates, isocyanates, carbamoyl chlorides, carbonates). The company operates in the Specialty Chemicals industry, serving pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, dyes/pigments and performance materials end‑use segments. It offers standard derivatives and custom synthesis/CRAMS for regulated customers across domestic and export markets. The company is part of the Alembic Group(Alembic Ltd is one of the oldest pharmaceutical companies in India) and has built a niche in hazardous phosgene chemistry with an integrated, safety‑led operating model.
Business Segments
- The company manufactures phosgene derivatives which are classified into 4 categories of Isocyanates , Chloroformates, Carbamates and Carbamoyl Chlorides.
- Phosgene is a colourless, odourless poisonous gas at room temperature, it needs to be cooled so that it turns liquid and can be transported easily. Phosgene was used as a chemical weapon during world war 1, where it was responsible for 85,000 deaths.

Liquified phosgene
(This is how it is transported)
- The chemistry of phosgene is quite simplified where only chlorine and carbon monoxide in presence of light is needed to make phosgene, however the high toxicity makes the chemistry difficult to handle.
High Toxicity
- The phosgene is a highly toxic gas and can result in extreme accidents if not handled properly.
- The bhopal gas tragedy in 1984 was a result of toxic gas leak of methyl isocynate.It was manufactured by Union Carbide which was used in agrochemical industry.
Less dependence on China
- The raw material required by Pasuahk is simply chlorine gas and carbon monoxide. Abundance of raw materials has reduced the dependency on China
- Shutdown of chinese chemical companies due to stricter environment norms are driving the demand.
- The labour cost (hourly cost of compensation) in China was lower than that of India till 2007. However, over 2005-2015, the average labour cost in China increased nearly 19-20%,against 4-5% CAGR in India. In fact, over the last five years, this cost has more than doubled compared with India.
End Industry
Isocyanates:
It is derived from synthesis of phosgene with amines and is majorly used in manufacturing of polyurethane and polycarbonate products. Polyurethane and polycarbonates are widely used in manufacturing foam mattresses. MDI (Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate) and TDI ( Toluene diisocyanate) are widely used in the Isocyanate family, however the company has forward integrated the value chain to manufacture high value products
Chloroformates:
Phosgene reacted with alcoholic functional group results in chloroformate products. Chloroformates have a wide range of applications as reagents in organic chemistry due to their nature of high reactivity. The intermediates are used in the manufacture of organic peroxide initiators for use in plastics and in activating groups used to make antibiotics and other pharmaceuticals. Some molecules also find application in the agrochemical industry where they are used in pesticides and insecticides.
Carbamates:
It is derived from synthesis of phosgene with diols. Carbamate derivatives are widely represented in agricultural chemicals, such as pesticides, fungicides, and herbicides. Some products are forward integrated from the existing basket. Acid Chlorides/ Carbamoyl : Reactive intermediates used to make esters, amides, ureas, and carbamates. Widely applied in agrochemicals; often forward integrated into finished actives due to high reactivity and handling challenges.
. Capacity Expansion
| Period (FY) | Installed phosgene capacity (MT/yr) | What changed / notes |
| 2014–2018 | 1,440 | Capacity steady at ~120 MT/month (1,440 TPA). |
| 2019–2021 | 4,800 | Capacity lifted to 4,800 TPA; unchanged through FY21 while planning the next expansion. |
| FY2022 (Q4)-FY 2025 | 14,400 | New 14,400 TPA phosgene plant commissioned; contributed from Q4 FY22. |
| FY2025–FY2026 (plan) | 14,400 (unchanged) | Capex of ~₹240 crore aimed at downstream capacity expansion and semi-specialized products (not a phosgene capacity increase). |
| Period (FY) | Installed phosgene capacity (MT/yr) | What changed / notes |
| 2014–2018 | 1,440 | Capacity steady at ~120 MT/month (1,440 TPA). |
| 2019–2021 | 4,800 | Capacity lifted to 4,800 TPA; unchanged through FY21 while planning the next expansion. |
| FY2022 (Q4)-FY 2025 | 14,400 | New 14,400 TPA phosgene plant commissioned; contributed from Q4 FY22. |
| FY2025–FY2026 (plan) | 14,400 (unchanged) | Capex of ~₹240 crore aimed at downstream capacity expansion and semi-specialized products (not a phosgene capacity increase). |
Polyurethanes markets
- The polyurethane market has one of the largest applications of phosgene and MDI and TDI are two major derivatives of phosgene used in this industry.
- MDI and TDI are used by foam making industries which are used in mattress, construction, cushions, automobiles, footwear etc and other foam products.
Top manufacturers of MDI and TDI
Covestro and BASF are the leading manufacturers of TDI and MDI with the highest global market share. The companies have some of the largest capacities for phosgene and use it captively for manufacturing products which have application in polyurethane and other industries.
MDI production in India
- GNFC manufactures TDI for and is one of the largest manufacturers in India, however the company is not backward integrated to manufacture phosgene.
- GNFC chemical business revenue in FY2021 contributed 64% to topline translate to value of 3305 Cr. TDI contributed 27% of chemical revenues translating to 892Cr.
Phosgene use in agrochemicals
- Derivatives of phosgene such as isocyanates, carbamates and chloroformates have a wide range of application in crop protection and technicals used in the agrochemical industry. The toxicity of phosgene makes it suitable for use in insecticides, herbicides and pesticides.
- Some companies using phosgene derivatives as raw materials.
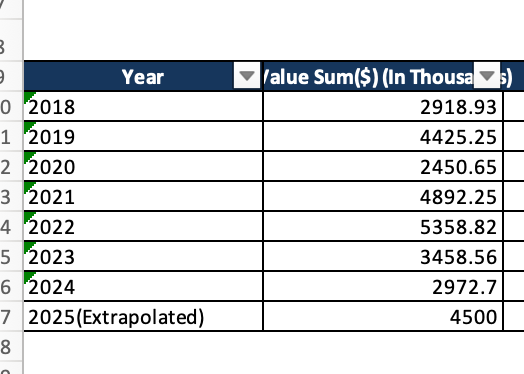
Shipping Data of Paushak

5. Manufacturing Units
Primary manufacturing complex at Panelav, Taluka Halol, Dist. Panchmahal (Gujarat); integrated site with phosgene generation, downstream MPP blocks, ETP/MEE, and safety systems. New multipurpose plant and R&D centre in the same ecosystem are under commissioning (FY26).
Certifications / Compliance – Responsible Care® ISO 9001/14001 / ISO 45001‑aligned IMS: regular audits; adherence to CWC and Indian Phosgene Council protocols.
Capex / Expansion Projects – FY25–FY26: Ongoing capex in downstream capacities and semi‑specialized products; commissioning of new MPP and advanced R&D centre targeted for FY26. – Budget/Mode: ~₹240 crore program over FY25–FY26
Note: Phosgene installed capacity stands at 14,400 tpa post approvals; downstream product‑wise capacities are not disclosed in AR.Why here / moat: – Scale & integration: In-house phosgene generation plus downstream multi-purpose lines → better supply reliability and cost control.
Custom development readiness: Multi-purpose assets suitable for client-specific molecules and multi-step chemistry, aiding ramp of CDMO.
6. Key Growth Drivers
- Capacity Expansion:
~₹240 cr program (FY25–FY26) to augment downstream capacities; commissioning of new MPP and R&D centre in FY26; expected to support higher volumes and more complex CRAMS.
- Agrochem and Pharma cycle turning around:
- Export: As the new expansion is coming in Phogene derivatives which is easier to transport compared to Phosgene. This provides opportunity to export which is also showing up in export data
- Sector tailwinds: China+1, import substitution, and safety‑critical sourcing requirements benefiting reliable domestic suppliers.
- CRAMS: This is a new segment that management is saying that they are foraying into but details not disclosed. CRAMS pipeline confidential.
Themes: – China+1 & domestic capex in pharma/agro supporting intermediate demand. – Polymer chain pull-through (PU/polycarbonate, autos, insulation, appliances) and electronics manufacturing (specialty polymers/coatings). – Import substitution aided by regulated handling where domestic specialists have an edge.
. Conclusion
Paushak is a structurally niche specialty chemical player with deep expertise in phosgene chemistry, strong compliance credentials, and a credible parentage (Alembic Group). Leadership transition has been orderly, with experienced operations and finance leaders in place.
The company is showing signs of turnaround back to growth and high margins due to agro and pharma cycle turning around and new plant coming live in FY26. Company in FY26 is commissioning milestones, product‑mix progression, and utilization ramp‑up. The ROCE profile (upper‑teens ) remains healthy for a niche player, and the FY25–FY26 capex aims to unlock volume/mix upside as new MPP/R&D assets come onstream. Also, export is expected to become a big opportunity going forward as mentioned by the management in the recent Annual Report. The promoter is starting to buy the stock. Though a lot of disclosure is not there, the signals are very positive.
Though there are execution risks and chemistry related risk which need to be monitored.
